Why Wearable Data is Messy and How to Normalize It
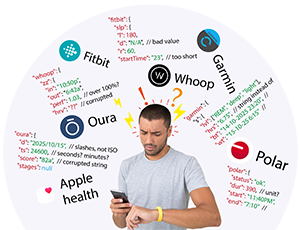
In the age of wearables and digital health, the amount of personal data generated by devices like Fitbit, Garmin, Apple Watch, and ŌURA is staggering. While these devices provide valuable insights into users' health, the data they generate often presents significant challenges.
One of the biggest obstacles developers face when integrating wearable data into apps is the messiness of the data itself. Wearables collect a wide variety of data from various sensors, but this data is often unstructured, inconsistent, and fragmented. The result? Developers spend a huge amount of time cleaning and normalizing data before it can be used for analysis and to generate actionable insights.
In this article, we will explore why wearable data is so messy, the challenges developers face, and how normalizing wearable data with one API can simplify the process and unlock the full potential of digital health applications.
Why is Wearable Data So Messy?
Different Devices, Different Formats
Each wearable device has its own method of collecting and storing data. Fitbit might track heart rate differently than Garmin or Apple Watch, and the way data is structured in their respective databases can vary significantly. For developers, this means they often need to account for multiple data formats and conversion challenges when pulling data from different devices.Unstructured Data
Much of the data generated by wearables is raw and unstructured. For example, heart rate data might come in the form of continuous time-series data, while sleep tracking data might be segmented into intervals of deep, light, or REM sleep. Without a standardized approach to organizing and categorizing this information, it’s difficult to aggregate and make sense of it across multiple sources.Inconsistent Measurements
Wearables are designed to provide estimates and trends rather than precise, medical-grade measurements. For example, a fitness tracker may estimate calories burned or distance traveled, but these numbers can vary based on device calibration, wear location, and the user’s activity level. This inconsistency can complicate the integration process and lead to inaccurate conclusions when comparing data across different devices or users.Volume of Data
Wearables are continuously collecting and transmitting data, which leads to an enormous volume of information. Managing the sheer amount of data generated by wearables can be overwhelming, especially when it needs to be processed in real-time for use in apps or clinical settings.
How to Normalize Wearable Data with One API
To overcome these challenges, developers need a way to standardize and normalize the data, making it easier to use, analyze, and integrate into applications. This is where a unified API comes in.
A unified API provides a way to aggregate data from different devices and normalize it into a consistent format. By using a single API, developers can access data from multiple wearables without needing to deal with the individual complexities of each device's data format.
Here’s how a unified API helps normalize wearable data:
Unified Data Structure
A unified API provides a standardized data structure that translates various data formats from different wearables into one consistent format. This eliminates the need for developers to write custom parsing code for each wearable device.Simplified Integration
Instead of integrating each wearable device’s API individually, developers can use a unified API to access data from multiple sources through a single integration point. This reduces the complexity of working with wearable data and speeds up the development process.Data Aggregation
The platform of a unified API aggregates data from multiple wearables and devices, providing a holistic view of the user's health. Whether it’s syncing data from a fitness tracker, smartwatch, or medical device, the API consolidates the information into one unified dashboard for easy analysis.Real-Time Data Processing
A unified API allows for real-time data streaming, enabling developers to create applications that can process wearable data instantly and provide personalized insights. Whether it's tracking heart rate variability during exercise or monitoring sleep patterns, real-time processing is essential for health apps that provide actionable feedback to users.Data Privacy and Security
As with any healthcare or personal data, data security is a top priority. A unified API ensures that all user data is handled in compliance with healthcare privacy standards like HIPAA and GDPR, providing a secure environment for storing and processing sensitive health data.
Benefits of Normalizing Wearable Data for Health Apps
Improved User Experience
When wearable data is consistent and easy to integrate, it allows developers to create more intuitive and responsive applications. Users will appreciate the personalized feedback that is generated from consistent, high-quality data.Faster Development Time
With normalized data, developers can focus more on creating features and user experiences rather than spending time cleaning and structuring raw data. This leads to faster development cycles and quicker time-to-market for health apps.Accurate Insights
Standardized data enables more accurate analytics, whether you’re tracking health metrics for fitness, chronic disease management, or wellness. By using consistent data across multiple devices, developers can build algorithms that provide deeper insights into users' health behaviors and needs.Scalability
As your app grows and integrates with more devices, having a unified API ensures that you can scale effortlessly. Instead of dealing with the complexities of integrating new devices, you can continue to rely on a unified API for seamless scalability.
Conclusion
Wearable data is a powerful tool for understanding health, but it can be messy and complex. By normalizing wearable data with one API, developers can overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of this valuable information. Platforms with unified APIs provide the foundation for building scalable, accurate, and data-driven health apps that deliver personalized experiences and actionable insights to users.
If you’re building a health app that integrates wearable data, consider using a unified API to simplify your development process and make sense of the data. By doing so, you’ll be able to create apps that empower users, improve health outcomes, and drive innovation in the health tech space.
Ready to simplify wearable data integration? Start today with a unified API!