Best Tools to Build AI Health Apps with Real-World Wearable Data
The integration of wearable data in healthcare apps has revolutionized the way we monitor and manage health. The ability to collect and analyze real-time physiological data such as heart rate, sleep patterns, physical activity, and even stress levels, has made it easier for individuals to take control of their health and well-being. Coupled with artificial intelligence (AI), these data streams can provide actionable insights, predictive analytics, and personalized recommendations, further empowering users to make informed health decisions.
In this article, we will explore the best tools and platforms available for building AI-powered health apps that leverage real-world wearable data, helping developers and organizations to create more effective, personalized, and data-driven health solutions.
1. ROOK API: Unified Wearable Data Integration
At the core of wearable health apps is the ability to integrate data from various sources and devices. The ROOK API offers a unified solution for developers to seamlessly connect and integrate wearable data from multiple devices like Fitbit, Garmin, Apple Watch, Dexcom, and ŌURA. By providing a single API, ROOK simplifies the complexity of data integration, allowing developers to focus on delivering personalized experiences rather than managing disparate data sources.
Why choose ROOK API for your AI health app?
Data Standardization: ROOK ensures that all wearable data is standardized, making it easier to analyze and use in AI algorithms.
Seamless Integration: With support for various wearable devices, it enables seamless integration into existing health and fitness apps.
Scalability: Whether you're targeting a few users or millions, the ROOK API scales with your app’s needs.
Security: Ensuring user data privacy and security is a top priority with ROOK’s secure data handling practices.
2. TensorFlow: AI for Health and Wearable Data Analysis
TensorFlow, developed by Google, is one of the most popular open-source platforms for building AI and machine learning models. TensorFlow is highly flexible and can be used for a wide range of applications, from building deep learning models to deploying AI algorithms. It is especially useful for analyzing large volumes of wearable data and uncovering insights from it.
Why use TensorFlow for wearable data analysis?
Flexibility: TensorFlow allows developers to create custom AI models that suit specific use cases, such as personalized health predictions or behavior analysis.
Prebuilt Models: TensorFlow offers pre-trained models for a variety of health-related applications, such as activity recognition and sleep tracking, that can be fine-tuned for wearable data.
Real-Time Data Processing: TensorFlow’s ability to handle real-time data processing is ideal for health apps that require live updates from wearable devices.
Cross-Platform Support: TensorFlow supports multiple platforms, from mobile to web, ensuring that your app runs smoothly across devices.
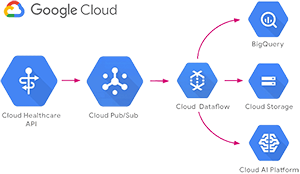
3. Google Cloud AI & Healthcare APIs
For developers building AI-powered health apps, Google Cloud AI & Healthcare APIs offer a robust suite of tools for integrating wearable data, analyzing it, and leveraging machine learning models. Google’s Healthcare API can help integrate, manage, and analyze health data, including data from wearables, in compliance with regulatory standards such as HIPAA.
Why choose Google Cloud AI & Healthcare APIs?
FHIR Compatibility: The Healthcare API is fully compatible with FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), the standard for electronic health records (EHRs), ensuring smooth integration of wearable data with other healthcare systems.
AI Models: Google’s pre-trained AI models can be used to analyze health data for tasks such as predictive analytics, early detection of diseases, and personalized health recommendations.
Scalable Infrastructure: Google Cloud’s infrastructure ensures that your app can scale to meet the growing demand for real-time health data analysis, whether for a small clinic or a global user base.
Security: With robust security features and compliance with global healthcare standards, Google Cloud ensures that sensitive health data is protected.
4. Microsoft Azure Health Data Services
Microsoft Azure Health Data Services provides a suite of tools for building AI-powered health apps, including APIs for healthcare data management, integration, and analytics. Azure’s tools can be particularly useful for integrating data from wearables into existing healthcare systems and improving decision-making through AI.
Why use Microsoft Azure Health Data Services?
Comprehensive Data Integration: Azure supports the integration of wearable data along with other health data sources, ensuring a comprehensive view of patients' health.
AI and Machine Learning: Azure’s built-in AI capabilities allow developers to create custom predictive models, analyze wearables data, and build smart health apps.
Interoperability: Azure ensures interoperability with existing healthcare systems, allowing seamless data exchange across platforms.
Data Security: Azure offers strong data encryption and complies with global healthcare regulations, ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive health data.
5. Apple HealthKit and ResearchKit
For developers building health apps specifically for the Apple ecosystem, HealthKit and ResearchKit are essential tools for working with wearable data. HealthKit allows you to access and integrate data from a wide range of Apple devices, including the Apple Watch, and use that data to deliver personalized health insights.
Why use Apple HealthKit and ResearchKit for wearable data?
Apple Device Integration: HealthKit makes it easy to integrate data from Apple devices and wearables like the Apple Watch into your app.
User-Centric Data: With HealthKit, developers can create apps that focus on specific health metrics, such as steps, heart rate, and sleep, and deliver personalized recommendations based on that data.
ResearchKit: If your app is focused on health research, ResearchKit allows you to collect data from participants in clinical studies and use AI to analyze that data.
Privacy and Security: Apple places a strong emphasis on user privacy, and HealthKit and ResearchKit comply with the highest data protection standards.
6. Fitbit Web API
Fitbit, one of the most well-known wearable brands, offers the Fitbit Web API, which allows developers to integrate Fitbit’s health and fitness data into their apps. This API provides access to a range of data, from activity tracking to heart rate monitoring, sleep data, and more.
Why use Fitbit Web API for health app development?
Extensive Data Access: The Fitbit Web API provides access to a wide variety of health data, enabling the development of highly personalized and data-driven fitness apps.
User-Friendly Integration: With easy-to-use API endpoints, developers can quickly integrate Fitbit data into their apps without a steep learning curve.
Customization: Developers can customize the data collected from Fitbit wearables and use AI to analyze it for creating personalized fitness plans, monitoring progress, and providing actionable insights.
Conclusion
Building AI-powered health apps that leverage real-world wearable data requires the right tools and platforms to integrate, analyze, and deliver personalized experiences. Whether you’re using ROOK’s API to simplify data integration, TensorFlow for deep learning, or Google Cloud for healthcare APIs, the tools mentioned above will enable you to create smarter, more effective health solutions.
As wearable technology continues to evolve, these platforms offer the flexibility and scalability necessary to turn wearable data into actionable insights that improve users' lives. So, whether you're in the fitness industry or working in digital health, these tools can help you stay ahead of the curve in building the next generation of health apps.